Edge computing processes data closer to its source, reducing latency and bandwidth use. It enhances efficiency and speed for real-time applications.
Edge computing is revolutionizing how data is handled. Traditional cloud computing sends data to centralized servers, which can cause delays. Edge computing brings data processing closer to the data source, minimizing latency. This is crucial for applications that require real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and IoT devices.
By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the load on central servers and improves overall network performance. This technology is essential for the future of fast, efficient, and reliable data management. Businesses are increasingly adopting edge computing to gain a competitive edge and deliver superior user experiences.
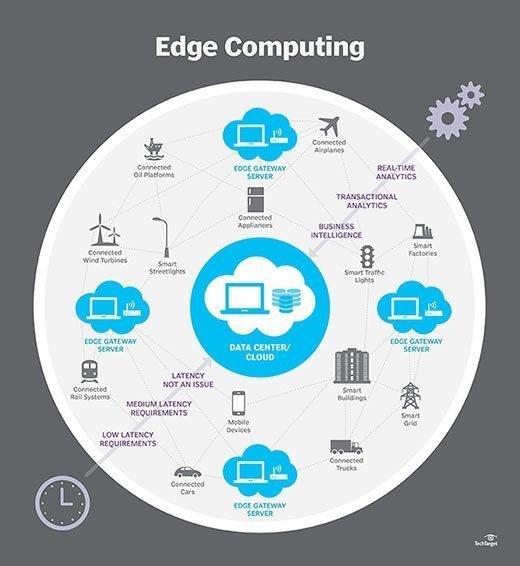
Credit: www.techtarget.com
Introduction To Edge Computing
Edge computing is a new way to process data. It brings computing closer to data sources. This method reduces latency and bandwidth use. It also improves speed and performance. Edge computing is crucial for modern technology.
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing processes data near the data source. This could be on devices, sensors, or local servers. Traditional computing uses centralized data centers. Edge computing, however, uses local nodes. These nodes handle data processing tasks.
Edge computing reduces the need for long-distance data transmission. This makes it faster and more efficient. It is very useful for real-time applications.
Importance In Modern Technology
Edge computing plays a big role in today’s tech world. It supports IoT devices, smart homes, and autonomous vehicles. These systems need fast data processing.
Here are some key benefits:
- Reduced Latency: Faster response times.
- Improved Bandwidth Usage: Less data sent to central servers.
- Enhanced Security: Data stays closer to its source.
- Scalability: Easier to add new devices.
| Traditional Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|
| Centralized data centers | Local nodes |
| Higher latency | Lower latency |
| More bandwidth needed | Less bandwidth needed |
How Edge Computing Works
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the data source. This reduces latency and improves performance. Let’s dive into the core components and data processing at the edge.
Core Components
Edge computing has several key components that work together:
- Edge Devices: These are sensors, cameras, and other IoT devices.
- Edge Nodes: These are local servers or gateways.
- Edge Networks: These connect edge devices to edge nodes and the cloud.
- Edge Applications: These run on edge nodes and process data locally.
Edge devices gather data from the environment. They then send this data to edge nodes. The edge nodes process and analyze the data. This reduces the load on the central cloud servers.
Data Processing At The Edge
Edge nodes handle most of the data processing tasks. This includes filtering, aggregating, and analyzing the data. Here’s how it works:
- Data Collection: Edge devices collect raw data from their surroundings.
- Data Transmission: This data is sent to edge nodes using edge networks.
- Data Processing: Edge nodes process the data locally to reduce latency.
- Data Storage: Processed data is stored locally or sent to the cloud.
- Data Analysis: Edge applications analyze the data in real-time.
Processing data at the edge has many benefits. It reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud. It also improves response times and enhances security.
Here is a table summarizing the core components and their roles:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Edge Devices | Gather data from the environment |
| Edge Nodes | Process and analyze data locally |
| Edge Networks | Connect devices to nodes and the cloud |
| Edge Applications | Run on nodes to process data |
Key Benefits
Edge computing is transforming the way data is processed. This technology brings computation and data storage closer to the data source. Let’s explore the key benefits of edge computing.
Reduced Latency
One of the most significant benefits of edge computing is reduced latency. Data is processed locally rather than traveling long distances. This local processing means faster response times. For example, in gaming, players experience less lag. In autonomous vehicles, decisions are made in real-time. This is crucial for safety and performance. Reduced latency is essential for applications requiring instant feedback.
Enhanced Security
Edge computing offers enhanced security by keeping sensitive data closer to the source. Data does not travel long distances, reducing exposure to cyber-attacks. Local data processing means fewer data breaches. This is vital for industries like healthcare and finance. They handle sensitive information daily. Enhanced security ensures data privacy and protection.
Applications Of Edge Computing
Edge Computing is transforming various industries by bringing computing power closer to data sources. This reduces latency and improves efficiency. Here are some key applications of Edge Computing:
Smart Cities
Smart Cities use Edge Computing to enhance urban living. Sensors and devices collect data in real-time. This data helps manage traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and improve public safety.
Traffic Management: Edge devices analyze traffic patterns. They adjust traffic signals to reduce congestion. This makes commuting faster and smoother.
Energy Efficiency: Smart grids use Edge Computing to monitor energy usage. They optimize electricity distribution. This reduces energy waste and costs.
Public Safety: Surveillance cameras with Edge Computing detect unusual activities. They alert authorities immediately. This enhances security and safety in urban areas.
Healthcare
Edge Computing is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling real-time data processing. This improves patient care and operational efficiency.
Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable devices track health metrics like heart rate and blood pressure. Edge devices process this data instantly. Doctors can monitor patients remotely and provide timely interventions.
Medical Imaging: Edge Computing accelerates the analysis of medical images. This speeds up diagnosis and treatment. It reduces the burden on central servers and minimizes delays.
Smart Hospitals: Edge devices manage hospital operations efficiently. They control lighting, temperature, and equipment usage. This enhances patient comfort and reduces operational costs.
Challenges And Limitations
Edge computing offers many benefits, but it also has its challenges and limitations. Understanding these can help in making informed decisions about its implementation.
Scalability Issues
One of the significant challenges in edge computing is scalability. Scaling involves adding more devices to handle increased data. This can be complex and costly. Each new device needs proper integration and maintenance.
A large number of edge devices need robust infrastructure. Without it, performance can suffer. Network bandwidth and latency also become concerns as the number of devices grows.
Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy is a critical issue in edge computing. Data is processed closer to where it is generated. This can lead to security vulnerabilities. Protecting data at multiple edge locations is challenging.
Data breaches can occur if edge devices are not secure. Ensuring all devices have up-to-date security measures is essential. Regular monitoring and updates are needed to protect sensitive information.
| Challenges | Details |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Adding more devices can be complex and costly. |
| Data Privacy | Protecting data at multiple locations is challenging. |

Credit: www.spiceworks.com
Edge Vs. Cloud Computing
Edge computing and cloud computing are two pivotal technologies. They transform how data is processed and managed. Understanding their differences helps choose the right solution for your needs.
Comparison Of Features
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing | Near the data source | At centralized data centers |
| Latency | Low | Higher |
| Scalability | Limited by local resources | Highly scalable |
| Security | Enhanced by local processing | Dependent on cloud provider |
| Reliability | Less dependent on internet | Dependent on internet connection |
Use Cases For Each
Edge Computing is ideal for applications needing real-time processing. Here are some examples:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Process data on the go for quick decisions.
- Smart Cities: Manage traffic and utilities with minimal delay.
- Industrial IoT: Monitor equipment in real-time to prevent failures.
Cloud Computing suits applications needing vast computational power. Here are some examples:
- Data Storage: Store and manage large datasets efficiently.
- Machine Learning: Train models with extensive computational resources.
- Web Applications: Deliver content globally with high availability.
Future Trends In Edge Computing
Edge computing is evolving rapidly. This evolution brings new trends and technologies. Two significant trends are integration with AI and the rise of 5G. These trends will shape the future of edge computing.
Integration With Ai
AI integration with edge computing offers powerful benefits. AI algorithms can process data locally at the edge. This reduces latency and enhances real-time decision-making. Examples include smart cameras, self-driving cars, and industrial robots.
AI at the edge also helps in predictive maintenance. Machines can predict failures before they happen. This reduces downtime and saves costs. Edge AI can also enhance security. It can detect threats and respond immediately.
5g And Edge
The rise of 5G networks will boost edge computing. 5G provides faster speeds and lower latency. This allows more data to be processed at the edge. Smart cities and IoT devices will benefit greatly.
5G and edge computing together enable real-time applications. These include augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and remote surgeries. The combination creates a powerful infrastructure for various industries.
Here’s a summary of the benefits:
| Trend | Benefits |
|---|---|
| AI Integration |
|
| 5G and Edge |
|
Getting Started With Edge Computing
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way data is processed. Instead of relying on centralized data centers, edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the data source. This reduces latency and improves performance.
To start with edge computing, you need the right tools, platforms, and best practices. Here, we will guide you through these essential elements.
Tools And Platforms
Several tools and platforms make edge computing easy. Here are some key ones:
- Raspberry Pi: A small, affordable computer for edge applications.
- NVIDIA Jetson: A platform for AI at the edge.
- Microsoft Azure IoT: A cloud service for edge computing solutions.
- AWS IoT Greengrass: A service for running local compute, messaging, and data caching.
These tools help you deploy and manage edge computing applications. Choose the one that fits your needs best.
Best Practices
Follow these best practices for effective edge computing:
- Start small: Begin with simple applications. Gradually scale up.
- Ensure security: Protect data and devices at the edge.
- Monitor performance: Regularly check the performance of edge devices.
- Optimize data flow: Minimize data transfer to reduce latency.
- Use containerization: Deploy applications in containers for flexibility.
Adopting these practices ensures a smooth edge computing experience. They help in achieving optimal performance and security.
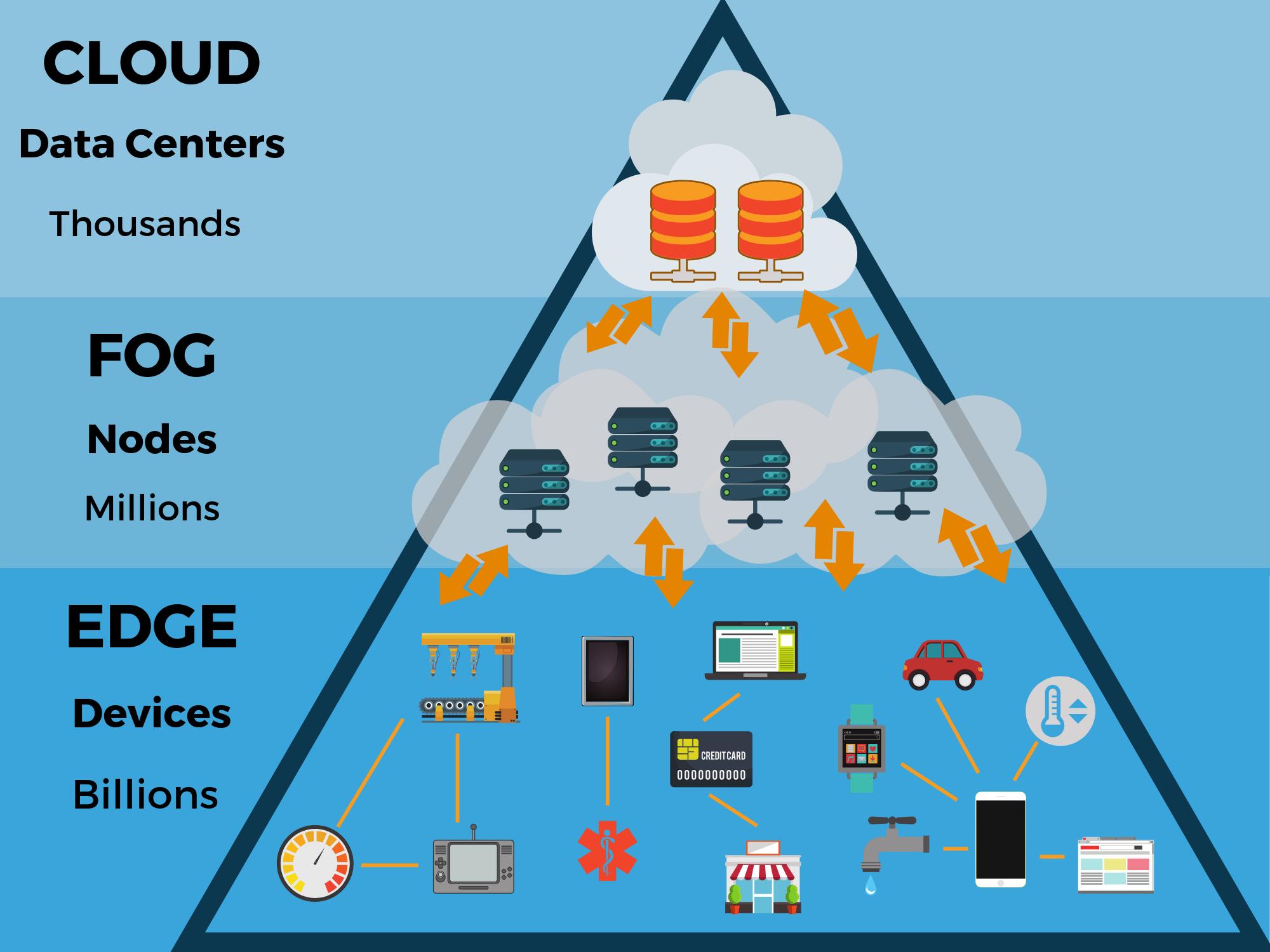
Credit: www.thinkebiz.net
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a technology that processes data closer to its source. It reduces latency and improves speed by minimizing data travel.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing works by processing data locally on edge devices. This reduces the need for data to travel to a central server, enhancing efficiency.
Why Is Edge Computing Important?
Edge computing is important because it reduces latency and bandwidth use. This leads to faster data processing and improved performance.
What Are The Benefits Of Edge Computing?
The benefits of edge computing include reduced latency, improved speed, enhanced data security, and better bandwidth management.
Conclusion
Edge computing is transforming data processing and storage. It brings computation closer to data sources, improving speed and efficiency. Businesses can benefit from reduced latency and enhanced security. As technology evolves, edge computing will play a crucial role. Stay informed and consider integrating edge computing into your strategy.
Embrace the future of data management.



